Cleanroom FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions About Cleanrooms
Frequently asked questions (and answers) to the most common interrogations related to cleanroom design, engineering, and manufacturing.
What is a Cleanroom?
To put it simply, a cleanroom is a room that is clean. An enclosed space in which the concentration of airborne particles is controlled, and constructed in a manner to minimize the introduction, generation, and retention of particles inside the room. Other parameters, such as temperature, humidity, and pressure, might be controlled as well, depending on the application and process.
What is a Modular Cleanroom?
What are ”Class 100”, ”Class 1,000”, ”Class 10,000” and ”Class 100,000” Cleanroom Classifications?
Class 100, Class 1000, Class 10,000 and Class 100,000 cleanrooms designate the maximum number of particles (0.5 micrometer (µm)) permitted per cubic feet of air in a cleanroom. In a Class 100 cleanroom, a maximum of 100 particles of 0.5 micrometer µm is permitted. Class 100, Class 1000, Class 10,000 and Class 100,000 are found in the Federal Standard 209 (FED-STE-209E) which was withdrawn in 2001 and officially replaced by ISO-14644-1 in 1999, but they are still widely used. The equivalent between FED-STE-209E and ISO-14644-1: 2015 is:
- Class 100 = ISO 5
- Class 1,000 = ISO 6
- Class 10,000 = ISO 7
- Class 100,000 = ISO 8
** Old FS 209 classes were calculated in cubic feet of air, whereas ISO classes are in cubic meter of air.
What is a Cleanroom Grade A, B, C and D?
In the sterile drug manufacturing industry, there are 4 grades: A, B, C and D.
- Grade A: The zone where the high-risk operations are made: the filing zone, stopper bowls, open ampoules and vials and aseptic connections. To conduct the process properly, those conditions are provided by a laminar airflow workstation. Grade A, both at rest and in operation, is equivalent to an ISO 5.
- Grade B: The background area to prepare the equipment going in the Grade A environment. It’s mainly for aseptic preparation and filling. At rest, Grade B is equivalent to an ISO 5, and in operation is equivalent to an ISO 7.
- Grade C and D: Cleanroom areas used for less critical stages in the manufacturing of sterile products. Grade C at rest is equivalent to an ISO 7 and in operation to an ISO 8. Grade D at rest is equivalent to an ISO 8.
The airborne particulate classification for grades A, B, C, D are given in the following table:
| Grade | Maximum permitted number of particles/m3 equal to or above | |||
| at rest | in operation | |||
| 0.5μm | 5.0μm | 0.5μm | 5.0μm | |
| A | 3,520 | 20 | 3,520 | 20 |
| B | 3,520 | 29 | 352,000 | 2,900 |
| C | 352,000 | 2,900 | 3,520,000 | 29,000 |
| D | 3,520,000 | 29,000 | not defined | not defined |
*Chart provided via:
https://www.canada.ca/content/dam/hc-sc/documents/services/drug-health-product-review-approval/compliance-enforcement/good-manufacturing-practices/guidance-documents/gmp-guidelines-annex-1-manufacture-sterile-drugs-0119/gui-0119-eng.pdf
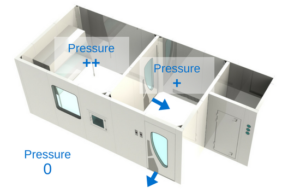
What is the difference between positive and negative pressure in cleanrooms?
Most cleanrooms are held in positive pressure. When dealing with hazardous contaminants, cleanrooms are usually held in negative pressure, eg. hazardous drug compounding and airborne infectious isolation rooms.
Positive pressure
Positive air pressure will make the airflow leak out of the room, instead of in, thus preventing unfiltered air or air particulates from entering the cleanroom. Simply put, to achieve positive pressure, more filtered air is pumped inside the clean zone to create a greater pressure differential than the adjacent, less clean rooms. Positive pressure is used in cleanrooms where the priority is keeping any germs or contaminants out of the cleanroom, to protect the manufacturing process.
Negative pressure
Negative pressure is used in cleanrooms to prevent potentially hazardous contaminated air, from escaping the room. Negative air pressure cleanroom means more air is pumped out of the room, rather than in, which makes the pressure lower than the adjacent environment, and serves to protect the user and the environment.